10 KiB
Raspberry Pi MQTT Monitor
The easiest way to track your Raspberry Pi or Ubuntu computer system health and performance in Home Assistant.
-
Monitor: cpu load, cpu temperature, free space, used memory, swap usage, uptime, wifi signal quality, voltage and system clock speed.
-
Supports discovery messages so no manual configuration in Home Assistant configuration.yaml is needed.
-
You can install it with just one command from shell.
-
Configurable: You can select what is monitored and how the message(s) is send (separately or as one csv message)
Table of Contents
- What is new
- Installation
- Configuration
- Test Raspberry Pi MQTT Monitor
- Schedule Raspberry Pi MQTT Monitor execution
- How to update
- Home Assistant Integration
- To Do
- Feature request
What is new
- 2021-01-27: Added a binary sensor for github to monitor for new versions of the script
- 2021-01-27: Updated the sensors names not to include the device name as per home assistant guidelines
- 2024-01-10: Added support for Raspberry Pi 5 fan speed monitoring (only works on Raspberry Pi 5 with stock fan)
Installation
Automated
Run this command to use the automated installation:
bash <(curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hjelev/rpi-mqtt-monitor/master/remote_install.sh)
Raspberry Pi MQTT monitor will be intalled in the location where the installer is called, inside a folder named rpi-mqtt-monitor.
The auto-installer needs the software below and will install it if its not found:
- python (2 or 3)
- python-pip
- git
- paho-mqtt
Only python is not automatically installed, the rest of the dependancies should be handeled by the auto installation. It will also help you configure the host and credentials for the mqtt server in config.py and create the cronjob configuration for you.
Manual
If you don't like the automated installation here are manuall installation instructions (missing the creation of virtual environment).
- Install pip if you don't have it:
sudo apt install python-pip
- Then install this python module needed for the script:
pip3 install paho-mqtt
- Install git if you don't have it:
apt install git
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/hjelev/rpi-mqtt-monitor.git
- Rename
src/config.py.exampletosrc/config.py
Configuration
(only needed for manual installation)
Populate the variables for MQTT host, user, password and main topic in src/config.py.
You can also choose what messages are sent and what is the delay (sleep_time is only used for multiple messages) between them.
If you are sending a grouped message, and you want to delay the execution of the script you need to use the random_delay variable which is set to 1 by default.
This is the default configuration (check the example file for more info):
random_delay = randrange(1)
discovery_messages = True
group_messages = False
sleep_time = 0.5
service_sleep_time = 120
cpu_load = True
cpu_temp = True
used_space = True
voltage = True
sys_clock_speed = True
swap = True
memory = True
uptime = True
wifi_signal = False
wifi_signal_dbm = False
rpi5_fan_speed = False
If discovery_messages is set to true, the script will send MQTT Discovery config messages which allows Home Assistant to automatically add the sensors without having to define them in configuration. Note, this setting is only available when group_messages is not used.
If group_messages is set to true the script will send just one message containing all values in CSV format.
The group message looks like this:
1.3, 47.1, 12, 1.2, 600, nan, 14.1, 12, 50, -60
Test Raspberry Pi MQTT Monitor
Run Raspberry Pi MQTT Monitor (you might need to update the path in the command below, depending on where you installled it)
/usr/bin/python3 /home/pi/rpi-mqtt-monitor/rpi-cpu2mqtt.py -d
Once you run Raspberry Pi MQTT monitor you should see something like this:
Hostname: ubuntu-pc
CPU Load: 30.8
CPU Temp: 66
Used Space: 11
Voltage: False
CPU Clock Speed: False
Swap: False
Memory: 65
Uptime: 0
Wifi Signal: False
Wifi Signal dBm: False
RPI5 Fan Speed: False
Git Update: on
Schedule Raspberry Pi MQTT Monitor execution
Create a cron entry like this (you might need to update the path in the cron entry below, depending on where you installed it):
*/2 * * * * cd /home/pi/rpi-mqtt-monitor; /usr/bin/python /home/pi/rpi-mqtt-monitor/rpi-cpu2mqtt.py
How to update
Navigate to the folder where Rapsberry Pi MQTT Monitor is installed and pull the git repository:
git pull
- Note that sometimes you might need to add new variables to our src/config.py file, so make sure you check the example file and update your config.py file accordingly.
Home Assistant Integration
If you are using discovery_messages, then this step is not required as a new MQTT device will be automatically created in Home Assistant and all you need to do is add it to a dashboard.
Once you installed the script on your raspberry you need to create some sensors in home assistant.
This is the sensors configuration if group_messages = True assuming your sensors are separated in sensors.yaml file.
- platform: mqtt
name: 'rpi4 cpu load'
state_topic: 'masoko/rpi4'
value_template: '{{ value.split(",")[0] }}'
unit_of_measurement: "%"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: 'masoko/rpi4'
value_template: '{{ value.split(",")[1] }}'
name: rpi4 cpu temp
unit_of_measurement: "°C"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: 'masoko/rpi4'
value_template: '{{ value.split(",")[2] }}'
name: rpi4 diskusage
unit_of_measurement: "%"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: 'masoko/rpi4'
value_template: '{{ value.split(",")[3] }}'
name: rpi4 voltage
unit_of_measurement: "V"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: 'masoko/rpi4'
value_template: '{{ value.split(",")[4] }}'
name: rpi4 sys clock speed
unit_of_measurement: "MHz"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: 'masoko/rpi4'
value_template: '{{ value.split(",")[5] }}'
name: rpi4 swap
unit_of_measurement: "%"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: 'masoko/rpi4'
value_template: '{{ value.split(",")[6] }}'
name: rpi4 memory
unit_of_measurement: "%"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: 'masoko/rpi4'
value_template: '{{ value.split(",")[7] }}'
name: rpi4 uptime
unit_of_measurement: "days"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: 'masoko/rpi4'
value_template: '{{ value.split(",")[8] }}'
name: rpi4 wifi signal
unit_of_measurement: "%"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: 'masoko/rpi4'
value_template: '{{ value.split(",")[9] }}'
name: rpi4 wifi signal
unit_of_measurement: "dBm"
This is the sensors configuration if group_messages = False assuming your sensors are separated in sensors.yaml file.
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: "masoko/rpi4/cpuload"
name: rpi4 cpu load
unit_of_measurement: "%"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: "masoko/rpi4/cputemp"
name: rpi4 cpu temp
unit_of_measurement: "°C"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: "masoko/rpi4/diskusage"
name: rpi4 diskusage
unit_of_measurement: "%"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: "masoko/rpi4/voltage"
name: rpi4 voltage
unit_of_measurement: "V"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: "masoko/rpi4/sys_clock_speed"
name: rpi4 sys clock speed
unit_of_measurement: "hz"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: "masoko/rpi4/swap"
name: rpi4 swap
unit_of_measurement: "%"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: "masoko/rpi4/memory"
name: rpi4 memory
unit_of_measurement: "%"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: "masoko/rpi4/uptime_days"
name: rpi4 uptime
unit_of_measurement: "days"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: "masoko/rpi4/wifi_signal"
name: rpi4 wifi signal
unit_of_measurement: "%"
- platform: mqtt
state_topic: "masoko/rpi4/wifi_signal_dbm"
name: rpi4 wifi signal
unit_of_measurement: "dBm"
Add this to your customize.yaml file to change the icons of the sensors.
sensor.rpi4_voltage:
friendly_name: rpi 4 voltage
icon: mdi:flash
sensor.rpi4_cpu_load:
friendly_name: rpi4 cpu load
icon: mdi:chip
sensor.rpi4_diskusage:
friendly_name: rpi4 diskusage
icon: mdi:harddisk
sensor.rpi4_sys_clock_speed:
icon: mdi:clock
sensor.rpi4_cpu_temp:
friendly_name: rpi4 cpu temperature
sensor.rpi4_swap:
icon: mdi:folder-swap
sensor.rpi4_memory:
icon: mdi:memory
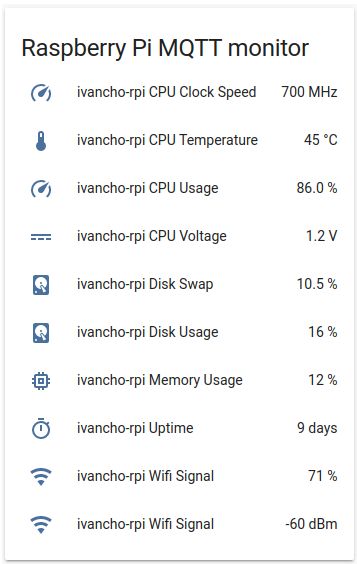
After that you need to create entities list via the home assistant GUI. You can use this code or compose it via the GUI.
type: entities
title: Rapsberry Pi MQTT monitor
entities:
- entity: sensor.rpi4_cpu_load
- entity: sensor.rpi4_cpu_temp
- entity: sensor.rpi4_diskusage
- entity: sensor.rpi4_voltage
- entity: sensor.rpi4_sys_clock_speed
- entity: sensor.rpi4_swap
- entity: sensor.rpi4_memory
- entity: sensor.rpi4_uptime
- entity: sensor.rpi4_wifi_signal
- entity: sensor.rpi4_wifi_signal_dbm
...
To Do
- maybe add network traffic monitoring via some third party software (for now I can't find a way to do it without additional software)
Feature request
If you want to suggest a new feature or improvement don't hesitate to open an issue or pull request.